Sampling-based
motion planning

MIT 6.821: Underactuated Robotics
Spring 2024, Lecture 18
Follow live at https://slides.com/d/syF900Q/live
(or later at https://slides.com/russtedrake/spring24-lec18)

Image credit: Boston Dynamics
Input: source \(v_s\), target \(v_t\), \(\tilde{g}\), \(\tilde{h}\), GetSuccessors()
Output: shortest path from \(v_s\) to \(v_t\)
\(p = \text{Path}([v_s])\)
\(S = \{ v_s : p \}\)
\(Q.\text{insert}(p)\)
while not \(Q.\text{empty}()\):
\(p = Q.\text{pop}()\)
\(u = p.\text{last}()\)
if \(u = v_t,\) then return \(p\)
for all \(v \in\) GetSuccessors\((u)\), where \(v \notin p\):
\(p' = \text{Path}(p, u)\)
if \(v \notin S\) or \(\tilde{g}(p') < \tilde{g}(S[v]),\):
\(S[v] = p'\)
\(Q.\text{insert}(p')\)
return failure
Visited dictionary
Priority queue using \(\tilde{f}\)
path with lowest \(\tilde{f}\)
Discrete A* algorithm
Motion planning as a (nonconvex) optimization
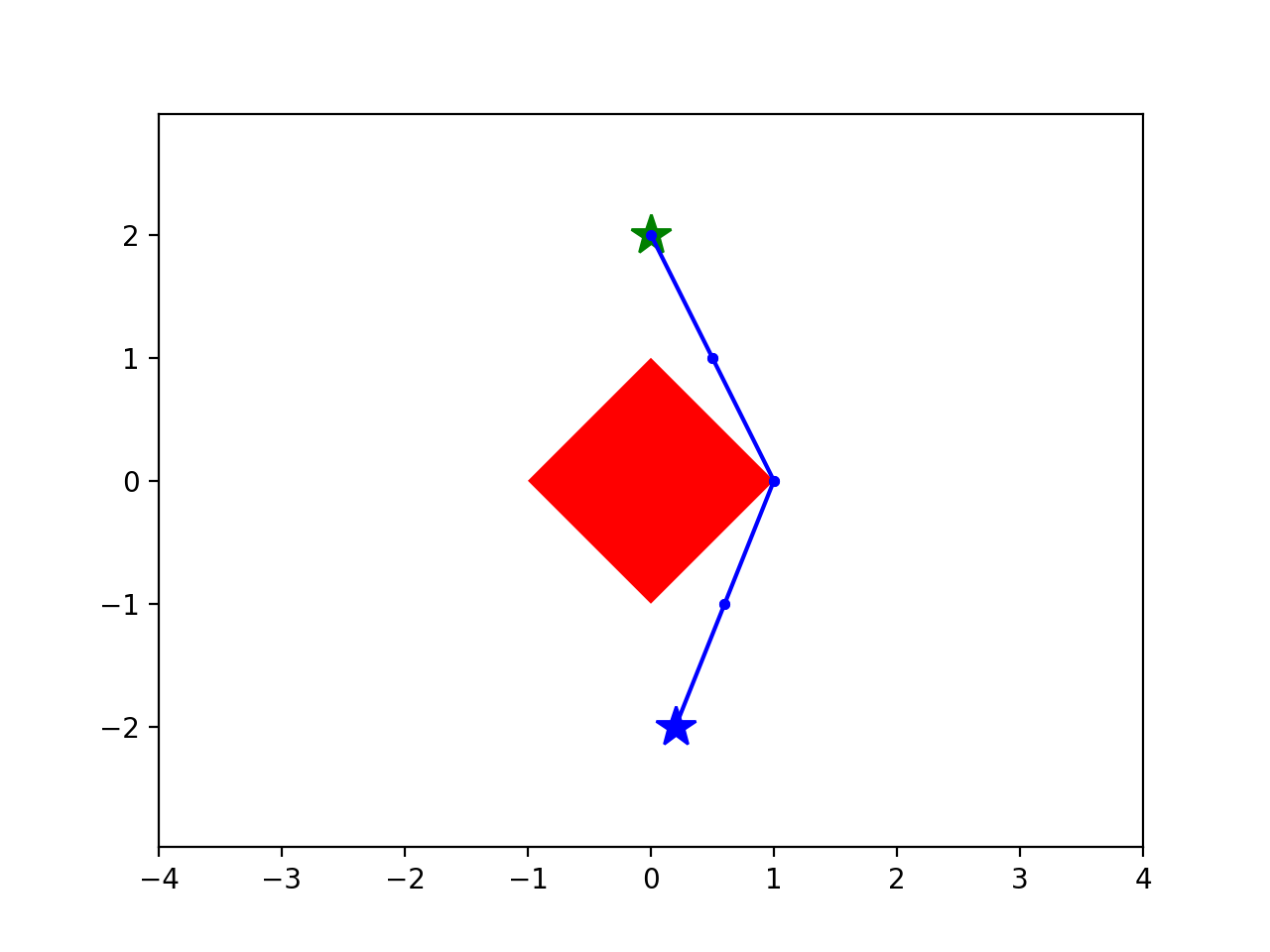
start
goal
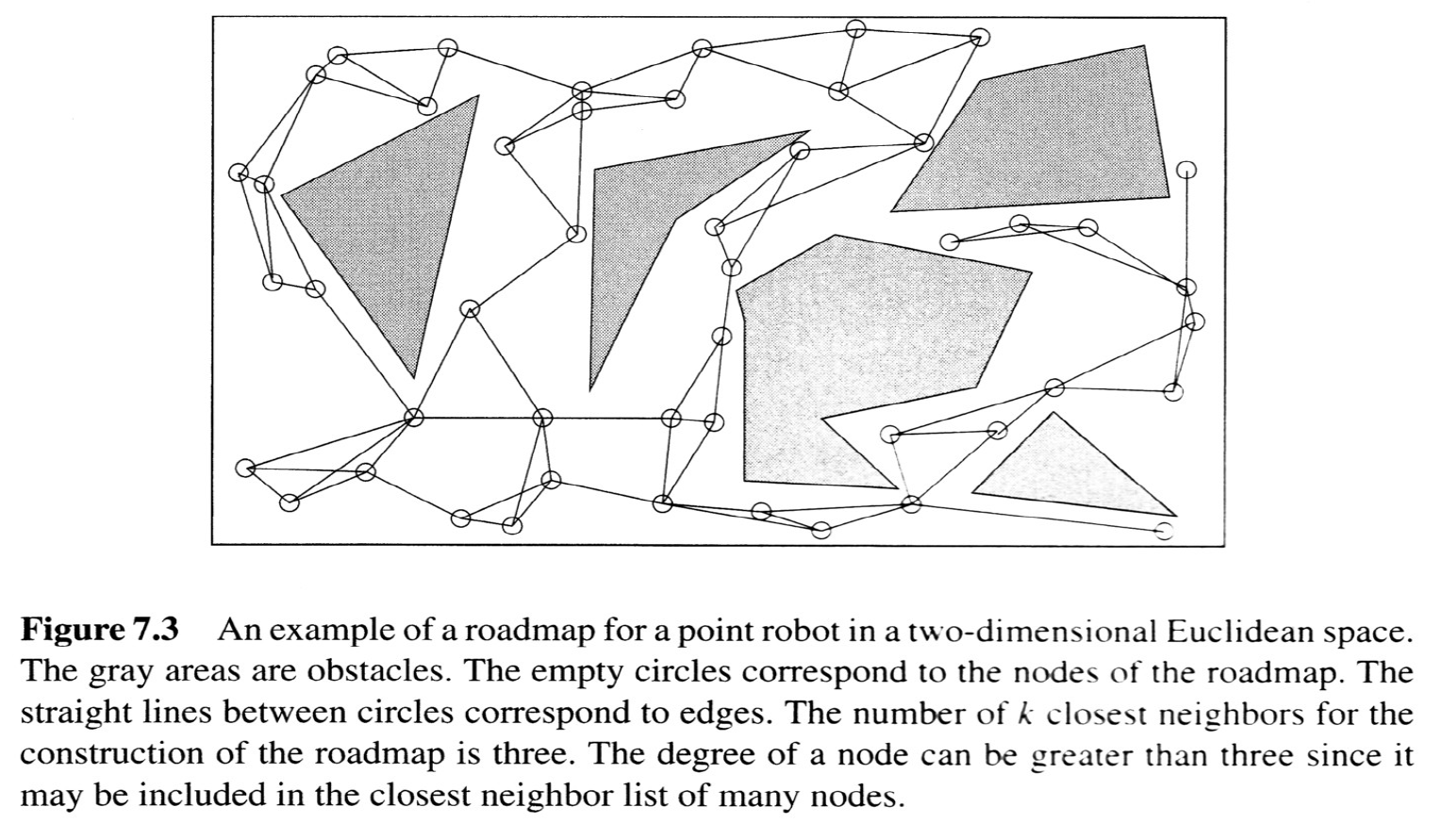
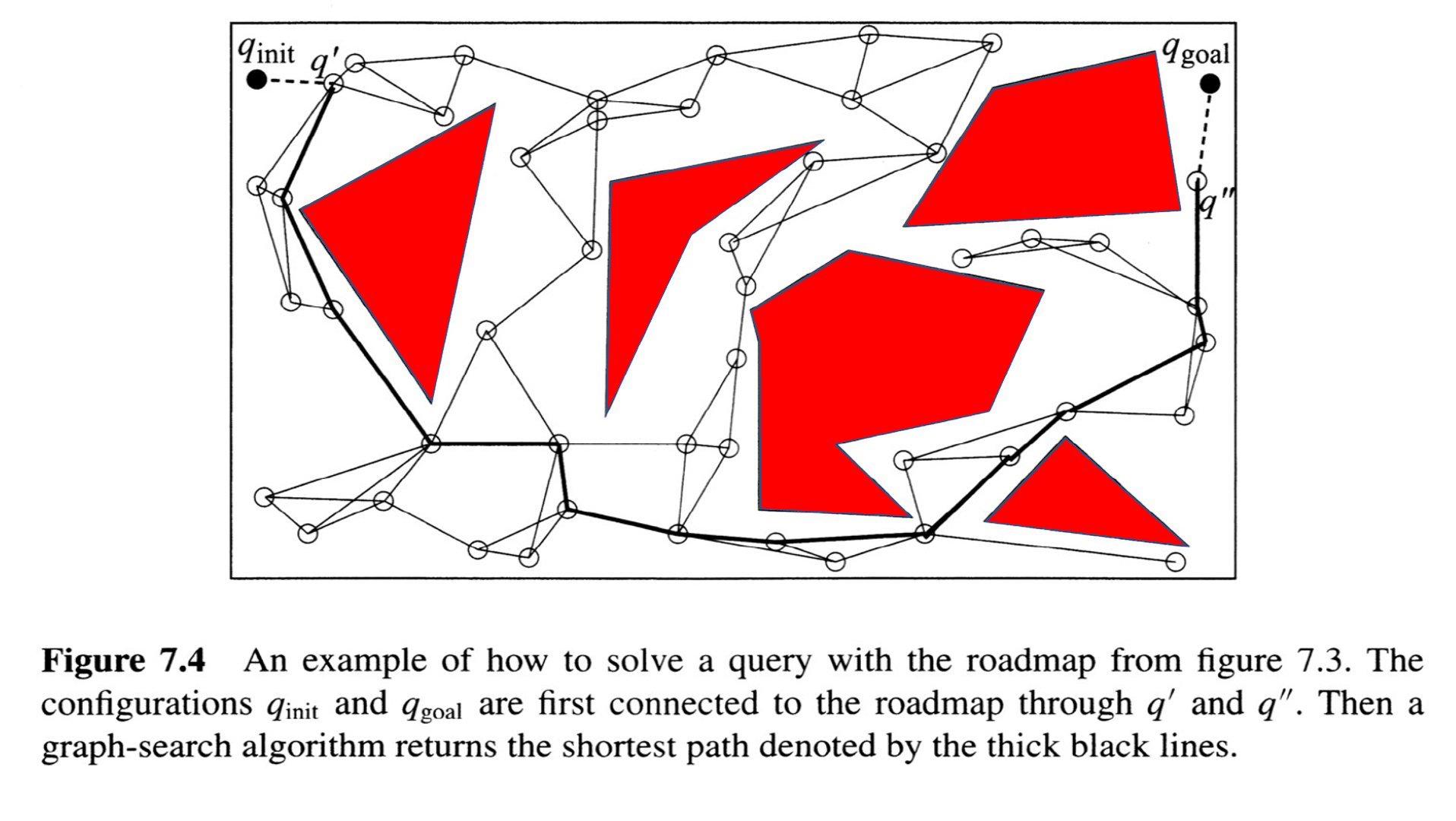
from Choset, Howie M., et al. Principles of robot motion: theory, algorithms, and implementation. MIT press, 2005.
Amato, Nancy M., and Yan Wu. "A randomized roadmap method for path and manipulation planning." Proceedings of IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. Vol. 1. IEEE, 1996.
BUILD_ROADMAP () {
V = {}, E = {}
for k = 1 to K
repeat
q = RANDOM_CONFIG()
until q is collision free
V.insert(q)
for all q in V
for all qn in NearestNeighbors(q, V)
if {q,qn} is collision free
E.insert({q,qn})
}Probabilistic Roadmap (PRM)
The Probabilistic Roadmap (PRM)
from Choset, Howie M., et al. Principles of robot motion: theory, algorithms, and implementation. MIT press, 2005.
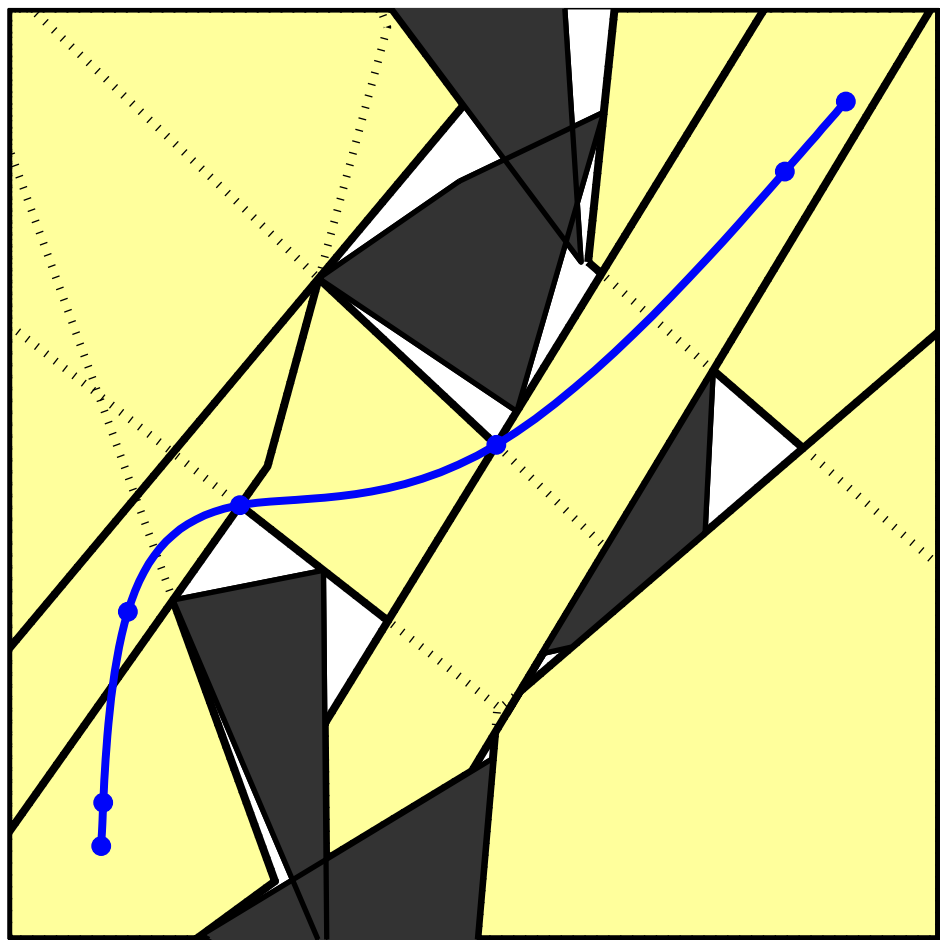
- PRM: A roadmap of points (vertices) connected by line segments
- GCSTrajOpt: A roadmap of convex sets (vertices) of continuous curves connected by continuity constraints
IRIS for Configuration-space regions
- IRIS (Fast approximate convex segmentation). Deits and Tedrake, 2014
- New versions work in configuration space:
- Nonlinear optimization for speed. IRIS-NP
- Sums-of-squares for rigorous certification. C-IRIS
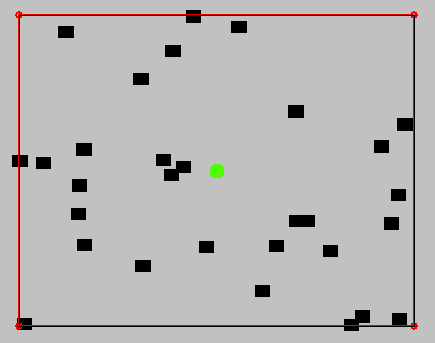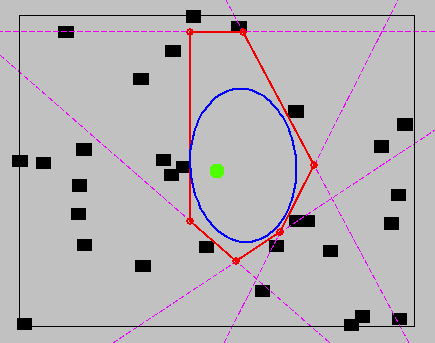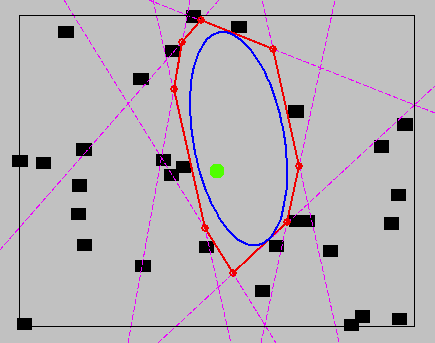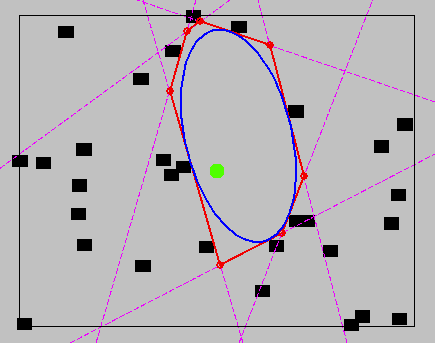
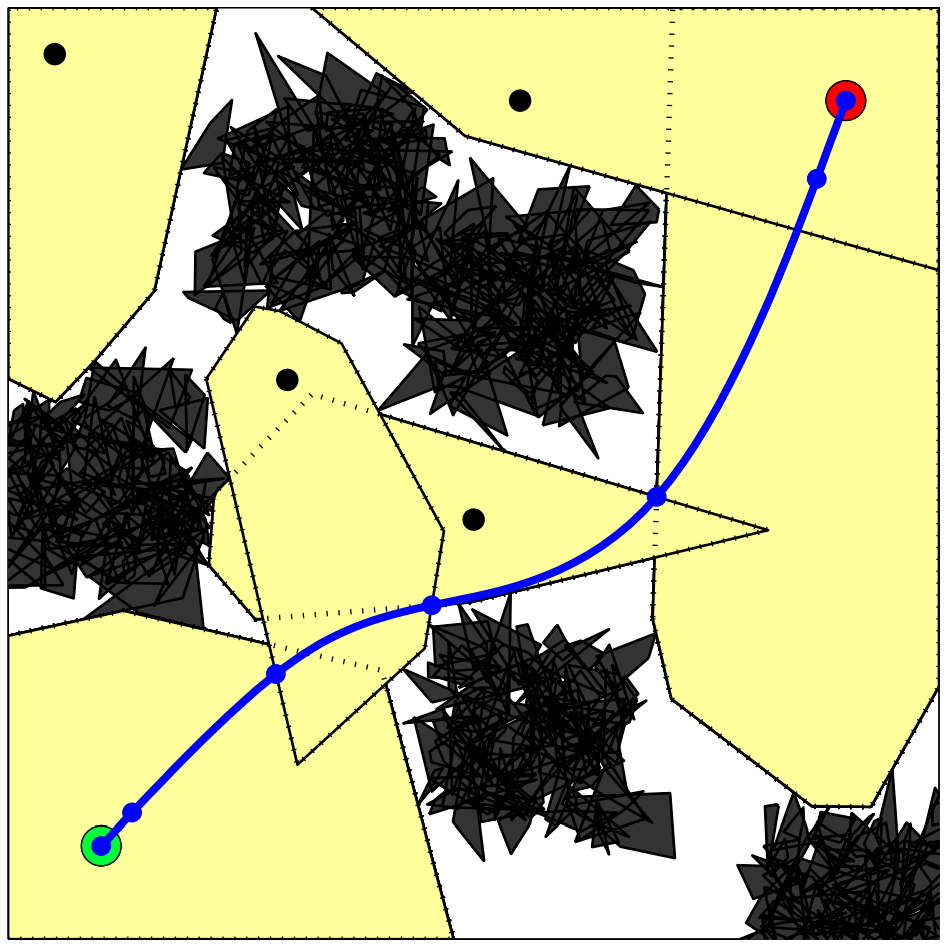
Convex decomposition of configuration space
- Naive sampling can lead to inefficient coverage
- New algorithms optimize a convex cover
- Insight: Cliques in the visibility graph (almost) correspond to convex sets in configuration space
- Approach: (Approximate) minimum clique cover

(Approximate) Minimum clique cover



Rapidly-exploring random trees (RRTs)
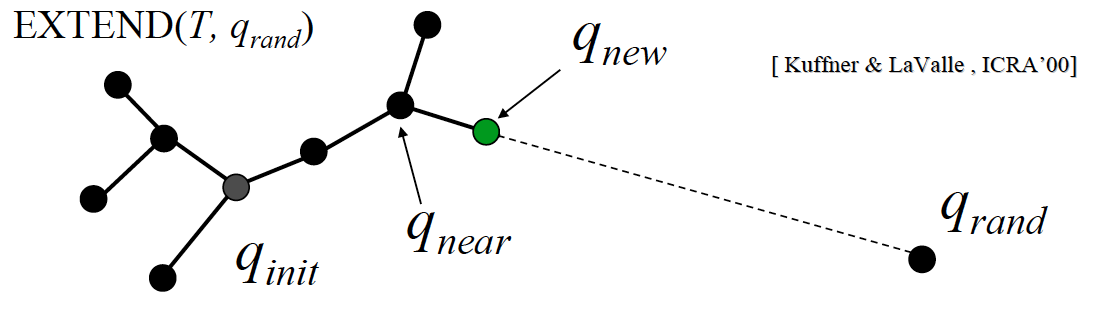
BUILD_RRT (qinit) {
T.init(q_init);
for k = 1 to K do
q_rand = RandomSample()
q_near = ClosestPoint(T, q_rand)
q_new = Extend(q_near, q_rand)
T.add(q_near, q_new)
}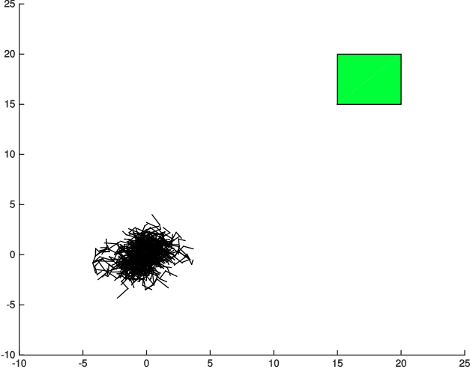
Naive Sampling
RRTs have a "Voronoi-bias"
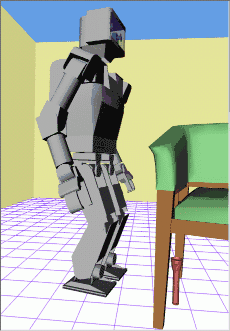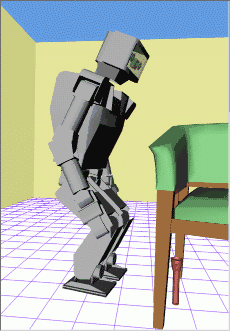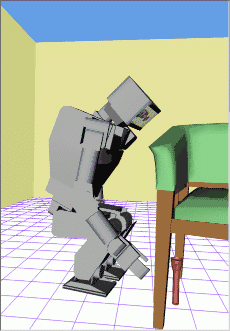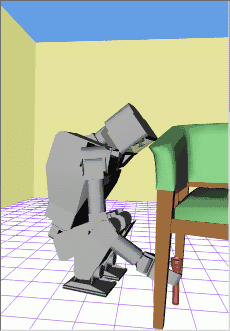
http://www.kuffner.org/james/plan


Cost-to-go for the obstacle-free case


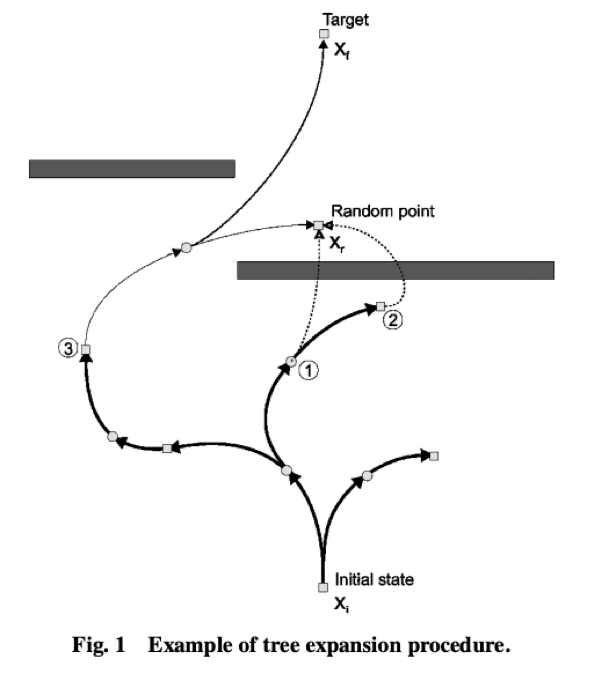
Basic RRT
Reachability-Guided RRT
Open Motion Planning Library (OMPL)
Google "drake+ompl" to find some examples (on stackoverflow) of drake integration in C++. Using the python bindings should work, too.


