Static Typing:
Which Language to Choose?

whoami?



- What is Hasura?
- Why do we want static typing?
- A walk through ReasonML, PureScript, TypeScript, and Elm.
- Comparison
- What did we choose and what's the plan?
Agenda

What is Hasura?
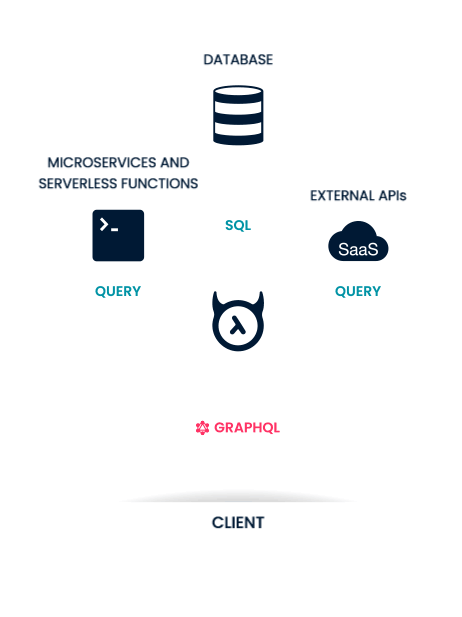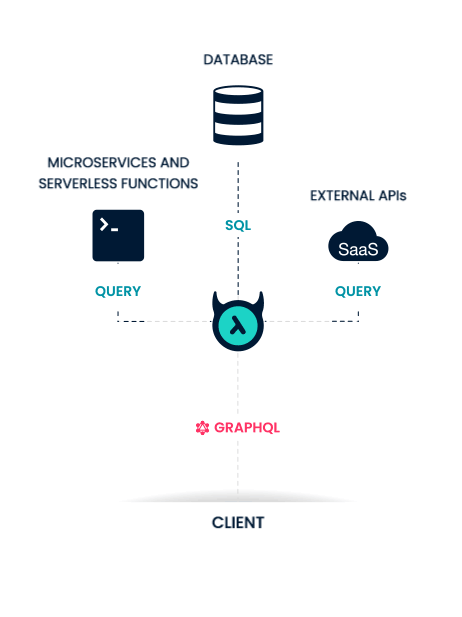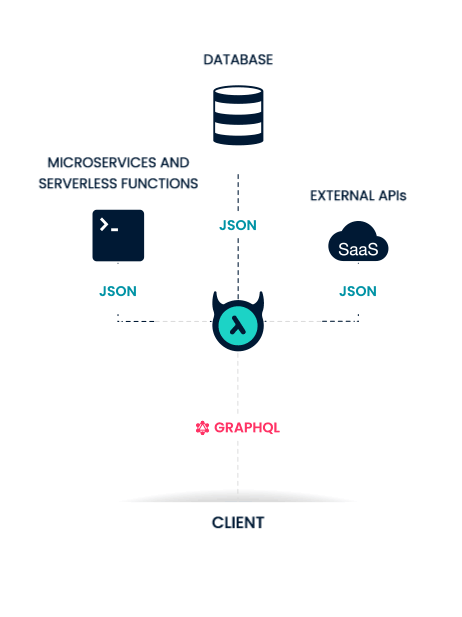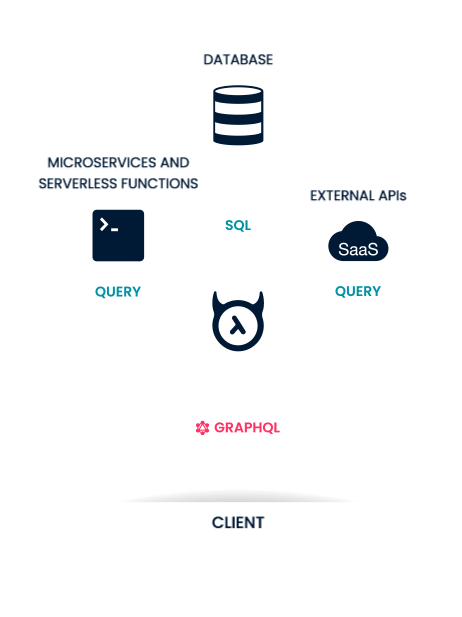
Why do we want
static typing?


JavaScript is not enough


null > 0; // false
null == 0; // false
null >= 0; // ???
// <- true
null > 0; // false
null == 0; // false
null >= 0; // true








😱


Dynamic typing is not enough


Dynamic typing is great for fast prototyping, testing ideas, but...


...as a project grows, it's not enough anymore.



At some point, control becomes crucial.
Ease of refactoring in a big codebase



Easier onboarding


Our backend is written in Haskell


JavaScript as a build target

A walk through ReasonML, PureScript, TypeScript, and Elm


import React, { useState } from "react";
export const Form = () => {
const [name, setName] = useState("");
const [password, setPassword] = useState("");
const onNameChange = e => {
setName(e.target.value);
};
const onPasswordChange = e => {
setPassword(e.target.value);
};
return (
<form>
<input
type="text"
placeholder="Name"
value={name}
onChange={onNameChange}
/>
<input
type="text"
placeholder="Password"
value={password}
onChange={onPasswordChange}
/>
<button type="submit" onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
Submit
</button>
</form>
);
};
Login form example
ReasonML
- Rock solid type system and strong type inference.
- Immutable and functional by default, but it supports mutations and side-effects.
- Reason supports React with ReasonReact and JSX syntax.


[@react.component]
let make = () => {
let (name, setName) = React.useState(() => "");
let (password, setPassword) = React.useState(() => "");
let onNameChange = (e: ReactEvent.Form.t): unit => {
let value = e->ReactEvent.Form.target##value;
setName(value);
};
let onPasswordChange = (e: ReactEvent.Form.t): unit => {
let value = e->ReactEvent.Form.target##value;
setPassword(value);
};
<form>
<input
type_="text"
name="name"
value=name
onChange=onNameChange
placeholder="Name"
/>
<input
type_="password"
name="name"
value=password
onChange=onPasswordChange
placeholder="Password"
/>
<button type_="submit"> {React.string("Submit")} </button>
</form>;
};
PureScript
- PureScript has a decent ecosystem.
- Great type system; provides features such as: typeclasses, higher kinded types, row polymorphism, higher-rank types, and many more.
- It's a purely functional and strict language.


module Form where
import Prelude
import Data.Maybe (fromMaybe)
import Effect (Effect)
import React.Basic.DOM as R
import React.Basic.DOM.Events (targetValue)
import React.Basic.Events (handler)
import React.Basic.Hooks (ReactComponent, component, useState, (/\))
import React.Basic.Hooks as React
form :: Effect (ReactComponent {})
form = do
component "form" \_ -> React.do
{ name } /\ setName <- useState { name: "" }
{ password } /\ setPassword <- useState { password: "" }
pure
$ R.form_
[ R.input
{ onChange:
handler targetValue \value ->
setName \_ -> { name: fromMaybe "" value }
, value: name
, placeholder: "Name"
}
, R.input
{ onChange:
handler targetValue \value ->
setPassword \_ -> { password: fromMaybe "" value }
, value: password
, placeholder: "Password"
}
, R.button
{ type: "submit"
, children: [ R.text "Submit" ]
}
]

TypeScript
- Superset of JavaScript
- Optional static typing
- There are many ways to adopt TypeScript.
- Zero configuration support in many modern IDEs.


import * as React from 'react';
export const Form: React.FC = () => {
const [name, setName] = React.useState('');
const [password, setPassword] = React.useState('');
const onNameChange = (e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
setName(e.target.value);
};
const onPasswordChange = (e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
setPassword(e.target.value);
};
return (
<form>
<input
type="text"
value={name}
onChange={onNameChange}
placeholder="Name"
/>
<input
type="password"
value={password}
onChange={onPasswordChange}
placeholder="Password"
/>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
);
};

Elm
- Purely functional language.
- Elm provides the ability to interoperate with JavaScript through ports and web components.
- A built-in architecture for organizing code makes managing data flow a breeze.


import Browser
import Html exposing (..)
import Html.Attributes exposing (..)
import Html.Events exposing (onInput)
main =
Browser.sandbox { init = init, update = update, view = view }
-- MODEL
type alias Model =
{ name : String
, password : String
}
init : Model
init =
Model "" ""
-- UPDATE
type Msg
= Name String
| Password String
update : Msg -> Model -> Model
update msg model =
case msg of
Name name ->
{ model | name = name }
Password password ->
{ model | password = password }
-- VIEW
view : Model -> Html Msg
view model =
Html.form []
[ viewInput "text" "Name" model.name Name
, viewInput "password" "Password" model.password Password
, button [] [ text "Submit" ]
]
viewInput : String -> String -> String -> (String -> msg) -> Html msg
viewInput t p v toMsg =
input [ type_ t, placeholder p, value v, onInput toMsg ] []
Comparison



Setup cost

Setup cost

ReasonML
3 steps:
npm install --save-dev bs-platform reason-react
{
"name": "your-project-name",
"reason": {
"react-jsx": 3
},
"sources": [
{
"dir": "src",
"subdirs": true
}
],
"suffix": ".bs.js",
"bs-dependencies": [
"reason-react"
],
"refmt": 3
}
Setup cost

PureScript
3 steps:
yarn global add purescript spago
yarn add -D purs-loader
spago init
spago install purescript-react-basic

Setup cost

TypeScript
6 steps:
yarn add -D typescript @babel/preset-typescript fork-ts-checker-webpack-plugin




{
"compilerOptions": {
"lib": ["es6", "dom", "es2017"],
"checkJs": true,
"allowJs": true,
"jsx": "react",
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true,
"strict": true,
"esModuleInterop": true,
"noEmitOnError": false
},
"exclude": ["node_modules"],
"include": ["src/**/*"]
}Setup cost

Elm
3 steps:
yarn add -D react-elm-components elm-webpack-loader{
"version": "0.0.1",
"type": "application",
"summary": "Elm <> Console",
"license": "Apache",
"source-directories": ["src/elm"],
"elm-version": "0.19.1",
"dependencies": {
"direct": {
"elm/browser": "1.0.0",
"elm/core": "1.0.0",
"elm/html": "1.0.0",
"elm/json": "1.0.0"
},
"indirect": {
"elm/time": "1.0.0",
"elm/url": "1.0.0",
"elm/virtual-dom": "1.0.0"
}
},
"test-dependencies": {
"direct": {},
"indirect": {}
}
}
Elm installed globally
Setup cost

Summary
JS interop

JS interop

module KnowMoreLink = {
[@bs.module "./KnowMoreLink.js"]
[@react.component]
external make: (
~href: string
~text: string = ?
) => React.element = "default";
};ReasonML
JavaScript in ReasonML
BuckleScript bindings

JS interop

ReasonML
ReasonML in JavaScript
import { make as User } from './User/index.bs';
const _ = <User />;JS interop

PureScript
JavaScript in PureScript
exports.unsafeHead = function(arr) {
if (arr.length) {
return arr[0];
} else {
throw new Error('empty array');
}
};foreign import unsafeHead :: forall a. Array a -> a
Foreign import declaration

JS interop

PureScript
PureScript in JavaScript
import { button as Button } from './Button/Button.purs';
<Button>Submit</Button>JS interop

TypeScript
JavaScript in TypeScript
// Dropdown.d.ts
type Props = {
options: Array<{ content: string }>;
dismiss(): void;
position: 'bottom' | 'right';
};
declare const Dropdown: React.FC<Props>;
export default Dropdown;-
allowJs: true
- Declaration file for JS code


JS interop

TypeScript
TypeScript in JavaScript

JS interop

Elm
JavaScript in Elm
var app = Elm.Main.init({
node: document.getElementById('elm'),
flags: locale
});1. Flags
2. Ports
var app = Elm.Main.init({
node: document.getElementById('elm')
});
app.ports.cache.subscribe(function(data) {
localStorage.setItem('cache', JSON.stringify(data));
});
app.ports.activeUsers.send(activeUsers);JS interop

Elm
Elm in JavaScript
import Button from './elm/Button.elm';
import Elm from 'react-elm-components';
<Elm src={Button.Elm.Main} />Migration cost

What did we choose and what's the plan?



We chose TypeScript
Hasura Console is a big, opensource project

Hasura Console is a big, opensource project
Low migration cost allows to keep velocity high.

Hasura Console is a big, opensource project
Low setup cost allows to keep velocity high.
Smallest difference between languages won't scare contributors.

- All new features in TypeScript
- Gradually adopt in the existing code
Adoption plan


Summary
What will you choose?

We chose TypeScript.
